Have you ever walked into a store and noticed how the products seem to be getting lighter, sleeker, and more colorful? Why does that bright, crinkly pouch on the shelf draw your eye more than the heavy, rigid container next to it? The truth is, flexible packaging is here, and it’s not just about looks. It’s a huge switch, from food and beverages to personal care and pharmaceuticals -- all industries are changing how businesses package and deliver products.
What is the reason for this sudden popularity? Businesses have a unique opportunity to use flexible packaging due to its combination of efficiency, sustainability, and innovation that traditional packaging just can’t. It is clear that something big is happening, as the global market is projected to reach USD 248.9 billion in 2022 and USD 315.5 billion by 2027. But why is flexible packaging so attractive to companies and consumers alike?
What is Flexible Packaging?

Flexible packaging is a type of packaging that can be easily bent or changed shape when filled or used. Flexible packaging is not rigid packaging, such as glass bottles or tin cans — it’s made from materials like plastic, paper, foil or a combination of these. These materials enable the package to be molded, folded, or wrapped in order to use.
Core Components of Flexible Packaging
- Plastic Films: Because of its durability and lightweight properties, common materials include polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), and polyethylene terephthalate (PET).
- Aluminum Foil: It offers a protective barrier against moisture, light, and oxygen.
- Paper and Laminates: Offer eco-friendly customizable packaging.
Flexible packaging is cheap and convenient for businesses to package their products, and for consumers to use.
What makes Flexible Packaging Better Than Other Options?

What’s the reason mylar bags has become the darling of industries compared to traditional packaging? This versatility and efficiency makes it the reason.
1. Lightweight and Portable
Flexible packaging is lightweight and easy to carry, unlike rigid packaging. Take for example a 1-liter stand-up pouch that weighs a lot less than a glass bottle of the same size.
2. Cost-Efficiency
Because it uses less raw material than rigid alternatives, flexible packaging is a less costly method in manufacturing as well as in shipping.
3. Enhanced Branding Opportunities
High-quality print of flexible materials such as films and laminates allows for more visually appealing products on the shelves.
4. Consumer Convenience
Flexible packaging is user-friendly due to features like resealable zippers, spouts, and easy tear openings. The convenience of being able to reseal the snack bag or pour liquid products is what customers love.
5. Sustainability
The use of fewer materials in flexible packaging means less waste. Many of the options are recyclable and the reduced weight means less carbon emissions during transportation.
Benefits of Flexible Packaging

Flexible packaging offers much more than its initial appeal. This has revolutionized the packaging world by providing solutions that address businesses, consumers, and the environment. Let’s explore the many advantages in detail:
1. Improved Shelf Life
Multi-layer films are flexible packaging materials that provide an exceptional barrier for moisture, air, and light. This is a protection that allows products such as snacks, coffee, or even medicine to remain fresh and continue quality longer. Vacuum-sealed flexible pouches can help extend the shelf life of perishable goods by protecting them from oxygen and contaminants.
2. Space Optimization
The cost advantages of flexible packaging help businesses. It is cheaper altogether because it uses fewer raw materials. Also, the lightweight design reduces shipping expenses. Flexible packaging is a budget-friendly but professional-looking solution for product presentation for small businesses. Flexible pouches for liquid products make more efficient use of space than bulky bottles.
3. Customization
The endless possibilities for customization in flexible packaging are through unique shapes, sizes, and finishes. High-quality printing can be used to make beautiful, attention-grabbing designs for brands. Matte or gloss finishes, and transparent windows for product visibility, all help create brand recognition with vibrant graphics.
4. Sustainability
Flexible packaging is quite eco-friendly. It uses less materials to minimize waste. In addition, the packaging is less energy and water-intensive than similar rigid packaging. Flexible packaging produces fewer greenhouse gases during manufacturing and transportation, making flexible packaging an environmentally sound choice, according to the Flexible Packaging Association (FPA).
5. Lightweight and Portability
The flexibility of flexible packaging allows for easier transport and easier handling for both businesses and consumers. The portability adds to user convenience, especially if you’re leading an on-the-go lifestyle, whether it’s a resealable snack bag or a spout pouch for baby food.
6. Reduced Carbon Footprint
Flexible packaging is also lighter and requires fewer transportation emissions than other packaging, making it a less carbon-intensive product overall. Research shows that switching from rigid to flexible packaging could cut emissions by as much as 60%.
Examples of Flexible Packaging
There are many forms of flexible packaging, all of which are tailored to meet the needs of a specific industry and specific product type. It is a preferred choice in all sectors due to its versatility. Below are some of the most common and innovative examples:
1. Stand-Up Pouches

These are some of the most popular types of flexible packaging.
- Uses: Snacks, soups, liquids, pet food, and frozen goods.
- Features: Equipped with resealable zippers or spouts, they offer convenience and prevent spillage. Their flat bottom design allows them to stand upright on shelves, increasing visibility.
- Example: A stand-up pouch for granola with a transparent window that shows the product inside.
2. Pillow Pouches

Pillow pouches are simple, cost-effective, and widely used.
- Uses: Chips, candies, spices, and frozen vegetables.
- Features: Lightweight and easy to manufacture, they are ideal for products requiring efficient mass production.
- Example: A potato chip bag with vibrant branding and airtight seals to keep contents fresh.
3. Retort Pouches
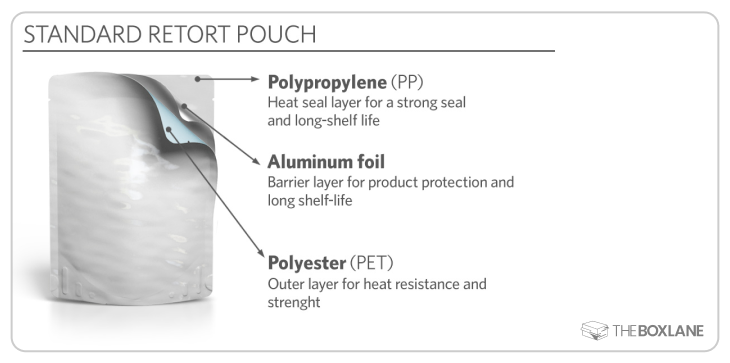
These high-performance pouches are designed to handle extreme conditions.
- Uses: Ready-to-eat meals, baby food, soups, and sauces.
- Features: They can withstand high temperatures during sterilization, making them ideal for long-shelf-life products.
- Example: A retort pouch for curry or stew, providing a lightweight alternative to traditional cans.
4. Sachets

Compact and single-use, sachets are perfect for portion-controlled packaging.
- Uses: Shampoo samples, instant coffee, ketchup, and medical creams.
- Features: Small, easy to open, and cost-efficient for single-use applications.
- Example: A hotel shampoo sachet or a single-serve instant coffee packet.
5. Shrink Films

Shrink films are used for bundling products together securely.
- Uses: Multi-packs of beverages, cosmetics, or electronics.
- Features: Heat-shrinkable, ensuring a tight fit around the products, enhancing protection during transit.
- Example: A six-pack of bottled water wrapped in durable shrink film.
6. Zip Lock Bags

These resealable bags are ideal for storing items that need to be accessed multiple times.
- Uses: Dry fruits, nuts, seeds, and craft supplies.
- Features: Airtight seals maintain freshness while offering user convenience.
- Example: A zip-lock bag for trail mix, with clear sides to showcase the product.
7. Blister Packs
Although primarily considered semi-flexible, blister packs often use flexible materials.
- Uses: Pharmaceuticals, small electronics, and batteries.
- Features: Protects items from contamination while offering visibility and tamper evidence.
- Example: A blister pack for vitamins, encased in a flexible foil backing.
8. Spouted Pouches
Spouted pouches are gaining popularity for liquid and semi-liquid products.
- Uses: Juices, baby food, yogurt, and cleaning detergents.
- Features: The built-in spout ensures easy pouring without spills.
- Example: A spouted pouch for energy gel or kids’ fruit puree.
9. Vacuum Bags
These are used to remove air from packaging to extend shelf life.
- Uses: Meat, seafood, coffee, and cheese.
- Features: Provides a tight seal, preserving freshness and preventing spoilage.
- Example: A vacuum-sealed coffee bag with a one-way valve to release natural gases.
10. Multi-Layer Laminated Films
These films are used for products requiring extra durability.
- Uses: Chips, cookies, and powdered products.
- Features: Offers excellent barrier properties against moisture, light, and odors.
- Example: A laminated bag of chocolate-covered pretzels.
Flexible Packaging is Used For

Flexible packaging is versatile and caters to a wide range of industries:
1. Food and Beverages:
Flexible packaging is well-known and widely used in the food and beverage industry because it preserves freshness and extends shelf life. It makes products stay fresh and easy to handle and store from snack pouches for chips, and cookies, to resealable coffee bags and juice packs.
2. Personal Care:
Flexible packaging is highly advantageous for the personal care sector because of its aesthetic appeal and practical design. As a result, these products are packaged in sachet or pouch form, with resealable features for convenient usage on travel and for everyday usage.
3. Pharmaceuticals:
In pharmaceuticals, flexible packaging ensures the safety, hygiene, and effectiveness of medical products. It’s commonly used for items such as liquid medicines, powders, tablets, and over-the-counter drugs. Sachets for electrolytes or single-dose medicine packs highlight the precise and protective nature of flexible materials.
4. Household Products:
Flexible packaging is a durable and user-friendly option for household products. This is widely used for detergents, cleaning agents, dishwashing liquids, and pet food. This category is particularly popular with packaging solutions like leakproof spouted pouches and stand-up designs.
5. Electronic and Small Industries:
Flexible packaging protects delicate items such as USB cables, headphones, chargers, etc. in electronics and small accessories. The electronic components are kept secure and free from damage in tamper-proof pouches and heat-sealed wraps.
6. Agriculture and Gardening Industry:
Flexible packaging also helps the agriculture and gardening industry to provide packaging for small gardening tools, seeds, and fertilizers. Waterproof, resealable bags make storing and carrying these items much easier while keeping their quality as original.
Flexible Packaging Films

Flexible packaging films are thin adaptable sheets of materials such as plastic, aluminum, or paper. These films have high value, being durable, lightweight, and excellent barriers, and this is useful for a variety of packaging applications. Below are additional types of flexible packaging films commonly used in industries:
- Polyethylene (PE): This film is widely favored for its flexibility, lightweight nature, and superior moisture resistance. It is commonly used for food packaging, shrink films and grocery bags.
- Polypropylene (PP): Known for its strength and transparency, polypropylene is ideal for packaging that requires clarity and heat resistance, such as snack wraps and bakery goods.
- Barrier Films: Designed to provide exceptional protection, these films shield products from oxygen, light, moisture, and aroma transfer. They are widely used in the food, pharmaceutical, and electronics sectors.
- Metalized Films: These films have a thin layer of metal, usually aluminum, applied to their surface. They are excellent for products requiring high barrier properties while maintaining lightweight packaging, such as chips and confectionery.
- Nylon Films (Polyamide): Nylon films are known for their toughness, puncture resistance, and clarity. They are often used in vacuum-sealed packaging for perishable foods like meat and cheese.
- Polyester Films (PET): Offering strength, durability, and clarity, PET films are often used for snack pouches, beverage labels, and laminated layers in multi-layer packaging.
- EVOH Films (Ethylene Vinyl Alcohol): These are high-performance films with superior oxygen barrier properties, making them suitable for perishable food products and medical supplies.
- Cellophane Films: Made from cellulose, these biodegradable films are a sustainable option often used for wrapping candies, bakery items, and gift packaging.
- PVC Films (Polyvinyl Chloride): PVC is highly versatile and used for shrink wraps, blister packs, and tamper-evident packaging due to its clarity and strength.
- Biodegradable and Compostable Films: Derived from materials like polylactic acid (PLA) or starch, these films cater to eco-conscious consumers, breaking down naturally in composting environments.
Manufacturing of Flexible Packaging

Flexible packaging manufacturing is a multi-step process that produces durable, functional, and attractive packaging solutions. Below is an in-depth explanation of each stage:
1. Material Selection
The selection of appropriate materials, usually plastics (polyethylene or polypropylene), paper, or aluminum (or a combination of these) is the first step.
- Criteria for Selection: That choice is determined by product requirements like moisture resistance, barrier protection, durability, and sustainability.
- Examples: If the snack is targeted to be a barrier against oxygen and moisture, then the material selected for these will be barrier films; but biodegradable materials can be selected for making eco-friendly products.
2. Printing
It gives packaging the branding, product information, and visual appeal.
- Printing Techniques: High precision and bright colors are achieved with the most commonly used methods (flexographic, gravure, and digital printing).
- Pre-Press Process: Design elements are prepared, color-separated, and adjusted for accuracy before they are printed.
- Quality Control: The visuals are inspected after printing to make sure they are aligned, colored, and sharp.
3. Lamination
Lamination involves bonding multiple layers of materials to enhance strength, durability, and barrier properties.
- Process: Layers of plastic, aluminum, or paper are adhered to using adhesives or heat to create a composite structure.
- Purpose: This step ensures the package can withstand physical stress, protect the contents from contamination, and maintain product freshness.
- Types of Lamination: Solvent-based, solvent-free, and water-based lamination are commonly used, depending on the application and environmental considerations.
4. Forming and Filling
Once laminated, the material is shaped into the desired packaging structure and filled with the product.
- Forming: Using specialized machines, the flat material is folded, sealed, or formed into shapes like pouches, bags, or films.
- Filling: The product (snacks, liquids, powders, etc.) is introduced into the formed package using automated filling machines for precision and efficiency.
- Customization: Features such as resealable zippers, spouts, or gussets are added during this stage if required.
5. Sealing
Sealing ensures the package is airtight, leak-proof, and tamper-evident.
- Sealing Methods: Heat sealing is the most common method, but ultrasonic and adhesive sealing are also used depending on the material.
- Purpose: Proper sealing prevents contamination, preserves freshness, and ensures product safety during transport and storage.
- Testing: After sealing, the package undergoes testing to confirm its integrity, ensuring no leaks or weak spots are present.
6. Final Inspection and Distribution
Before shipping, the finished packaging undergoes a final inspection to ensure quality standards are met.
- Inspection Criteria: Factors like print accuracy, seal strength, and overall appearance are checked.
- Packaging: Completed packages are boxed and prepared for transport to manufacturers or distributors.
Recycling of Flexible Packaging

Recycling flexible packaging presents a unique challenge due to the combination of various materials like plastics, aluminum, and paper, which are often layered together to enhance functionality, such as moisture and oxygen barriers. This multi-material structure makes it difficult to separate during the recycling process, complicating efforts to properly recycle these packages. Additionally, contamination from food residue and the lack of specialized equipment in traditional recycling facilities further exacerbates the problem. However, the industry is making strides to overcome these challenges.
One key innovation is the development of mono-material packaging, where single materials like polyethylene (PE) are used, making them easier to recycle. These materials are designed to provide similar barrier properties as multi-layer films but without the complexity of mixed materials. Additionally, organizations like TerraCycle are working to create programs that help consumers recycle flexible packaging, and advancements in flexible packaging recycling technologies are slowly making it easier for the industry to handle these materials more sustainably.
Flexible Packaging Market and Future

The flexible packaging market is experiencing significant growth and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.8% from 2022 to 2027. This growth is fueled by the increasing demand for convenience, product preservation, and customization in packaging. As consumer preferences shift toward eco-friendly solutions, flexible packaging is emerging as a popular choice due to its lightweight nature, cost-effectiveness, and ability to reduce waste compared to rigid alternatives. Industries across food, beverages, pharmaceuticals, and personal care are adopting flexible packaging to meet these evolving consumer needs.
Looking ahead, sustainability will be a key driver for innovation in the flexible packaging industry. As environmental concerns grow, there will be a stronger focus on developing recyclable, biodegradable, and mono-material packaging solutions. This will lead to advancements in material technology, including the use of plant-based plastics and improvements in recycling processes to handle flexible packaging more effectively. In addition, design innovation will continue to play a crucial role, with packaging becoming more efficient, functional, and visually appealing while minimizing its environmental footprint. These trends suggest a dynamic and sustainable future for flexible packaging.
Conclusion
Flexible packaging is more than a trend—it's a revolution in the packaging industry. With its versatility, cost-efficiency, and sustainability, it’s no wonder flexible packaging is taking over shelves across industries. Businesses looking to stay competitive should consider investing in flexible packaging solutions to meet consumer demands for convenience and eco-friendliness. As the market evolves, the future of packaging looks lighter, brighter, and more flexible.
At The Box Lane, we offer innovative and customizable packaging solutions tailored to your business needs, ensuring you stay ahead in this rapidly changing market.


